
Bind Python & SystemVerilog
What is PyStim?
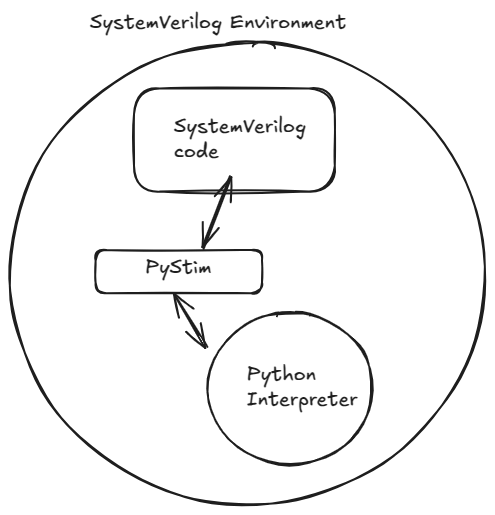
PyStim is SystemVerilog library that enables seamless interoperability between Python and SystemVerilog. Essentially, it allows to create SystemVerilog bindings for Python code, making it possible to call Python functions, use Python classes, and execute Python scripts within the SystemVerilog environment. The PyStim library allows Python code to run directly within a SystemVerilog environment by embedding a Python interpreter. The library binds Python & SystemVerilog in one component.
Why Use PyStim?
Harness Python’s full power in SystemVerilog with PyStim.
A Brief Look
Integrate Python with SystemVerilog
The subsequent code snippet demonstrates the use of PyStim to invoke the factorial function provided by Python’s math module.
import pystim_pkg::*;
module math_factorial();
typedef pystim_pkg::pystim py;
initial begin
automatic py_object result_obj;
py::initialize_interpreter();
result_obj = py_module::import_("math").attr("factorial").call(py::int_(4));
$display("Result: factorial(4) = %0d", result_obj.cast_int().get_value());
py::finalize_interpreter();
end
endmoduleLine 8: `py::initialize_interpreter()` intilize Python interpreter. This step is crucial as it sets up the environment for executing Python code.
Line 10: Code imports the Python “math” module and calls its “factorial” function with the argument “4”. The result of this function call is stored in `result_obj`. The py::int_(4) function converts the integer into a System Verilog Python integer object wrapper.
Line 11: The `result_obj.cast_int().get_value()` chain converts the Python object back into a SystemVerilog integer.
Line 13: Finally, the Python interpreter is finalized and cleaned up using `py::finalize_interpreter()`, ensuring that all resources are properly released.
The code demonstrates how to integrate Python functionality within a SystemVerilog environment. It leverages Python’s extensive libraries to perform complex calculations that might be cumbersome to implement directly in SystemVerilog.